Highlights:
SD-WAN (appliance + control and management software) revenue reached $116M in 3Q17, up 18% quarter-over-quarter (QoQ) and up 2.8x year-over-year (YoY). VeloCloud led the SD-WAN market with 22% share of 3Q17 revenue, Aryaka was in second place with 18%. Silver Peak rounded out the top 3 with 12%, according to the DC Network Equipment market tracker early edition from IHS Markit.
“The majority of SD-WAN solutions at first focused on virtualizing the WAN connection problem bringing automation, reliability, and agility to the enterprise WAN using overlays. Current use cases include direct connect for branch offices to the Internet and increased reliability through automated fail-over for a better user experience,” said Cliff Grossner, Ph.D., Senior Research Director and Advisor for the Cloud and Data Center Research Practice at IHS Markit.
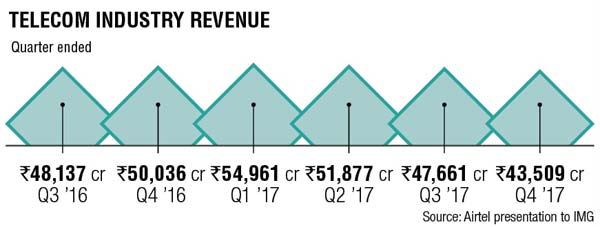
Worldwide SD-WAN revenue (US$M)-3Q-2017:
|
VeloCloud |
|
$26.0 |
|
|||
|
Aryaka |
|
$21.3 |
|
|||
|
Silver Peak |
|
$14.1 |
|
|||
|
Viptela |
|
$9.5 |
|
|||
|
InfoVista |
|
$4.4 |
|
|||
|
Citrix |
|
$4.4 |
|
|||
|
Talari |
|
$4.1 |
|
|||
|
TELoIP |
|
$3.9 |
|
|||
|
FatPipe |
|
$3.8 |
|
|||
|
Cisco |
|
$3.1 |
|
|||
|
Huawei |
|
$2.8 |
|
|||
|
CloudGenix |
|
$2.5 |
|
|||
|
Riverbed |
|
$1.7 |
|
|||
|
ZTE |
|
$0.6 |
|
|||
|
Other |
|
$14.2 |
|
|||
|
Total SD-WAN |
$116.2 |
|||||
| Source: IHS-Markit | ||||||
“With the WAN connectivity problem well understood and solutions ramping in deployments, SD-WAN vendors are beginning to offer additional services such as WAN optimization and virtual firewall. The next important challenge for SD-WAN vendors to solve is providing connectivity with SLAs and security for the multi-cloud,” said Cliff Grossner.
More Market Highlights:
· 3Q17 ADC revenue increased 5% from 2Q17 and decreased 5% from 3Q16
· Virtual ADC appliances stood at 28% of 3Q17 ADC revenue
· F5 garnered 45% ADC market share in 3Q17 with revenue down 4% YoY. Citrix had the #2 spot with 29% of revenue, and A10 (8%) rounded out the top 3 market share spots.
Data Center Network Equipment Report Synopsis:
The IHS Markit Data Center Network Equipment market tracker is part of the Data Center Networks Intelligence Service and provides quarterly worldwide and regional market size, vendor market share, forecasts through 2021, analysis and trends for (1) data center Ethernet switches by category [purpose built, bare metal, blade and general purpose], port speed [1/10/25/40/50/100/200/400GE] and market segment [enterprise, telco and cloud service provider], (2) application delivery controllers by category [hardware-based appliance, virtual appliance], and (3) software-defined WAN (SD-WAN) [appliances and control and management software]. Vendors tracked include A10, ALE, Arista, Array Networks, Aryaka, Barracuda, Cisco, Citrix, CloudGenix, Dell, F5, FatPipe, HPE, Huawei, InfoVista, Juniper, KEMP, Radware, Riverbed, Silver Peak, Talari, TELoIP, VeloCloud, Viptela, ZTE and others.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
From a Nov 15, 2017 press release:
According to the IHS Markit Data Center and Enterprise SDN Hardware and Software Biannual Market Tracker, SD-WAN is currently a small market, totaling just $137 million worldwide in the first half of 2017 (H1 2017). However, global SD-WAN hardware and software revenue is forecast to reach $3.3 billion by 2021 as service providers partner with SD-WAN vendors to deploy overlay solutions — and as virtual network function (VNF)–based solutions become more closely integrated with carrier operations support systems (OSS) and business support systems (BSS).
“Currently, the majority of SD-WAN revenue is from appliances, with early deployments focused on rolling out devices at branch offices,” Grossner said. “Moving forward, we expect a larger portion of SD-WAN revenue to come from control and management software as users increasingly adopt application visibility and analytics services.”
More highlights from the IHS Markit data center and enterprise SDN report:
- Globally, data center and enterprise software-defined networking (SDN) revenue for in-use SDN-capable Ethernet switches, SDN controllers and SD-WAN increased 5.4 percent in H1 2017 from H2 2016, to $1.93 billion
- Based on in-use SDN revenue, Cisco was the number-one market share leader in the SDN market in H1 2017, followed by Arista, White Box, VMware and Hewlett Packard Enterprise
- Looking at the individual SDN categories in H1 2017, White Box was the frontrunner in bare metal switch revenue, VMware led the SDN controller market segment, Dell held 45 percent of branded bare metal switch revenue and Hewlett Packard Enterprise had the largest share of total SDN-capable (in-use and not-in-use) branded Ethernet switch ports
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Editor’s Notes:
We’ve repeatedly pounded the table that there are no standards for SD-WANs, despite efforts by MEF [1]. That implies single vendor SD WAN with vendor lock-in and no interoperability between SD-WANs from different vendors.
Note 1. MEF says it will standardize the managed services that SD-WAN network operators deliver, by developing open APIs, along with common terminology and components. This effort builds on MEF’s Lifecycle Service Orchestration effort. Please refer to this MEF document.
Note 2. Gartner’s definition of SD-WAN

More from Gartner on SD-WANs:
Enterprise network leaders face enormous challenges adapting and changing their managed WAN services to meet constantly changing business needs for new applications, new offices, more users, cloud services and digital business. Based on hundreds of client inquiries and recent Research Circle surveys, a key obstacle is that traditional network services are too slow in meeting these needs, and network leaders need alternative solutions that can meet their evolving needs faster. Compared to traditional WAN services, managed SD-WAN services (including various WAN connectivity services) are emerging with promises of greater agility, flexibility, control and cost-efficiency.
Gartner recommends that network leaders seeking managed WAN services use end-to-end managed SD-WAN and connectivity services to create agile and cost-effective managed WAN services. However, they must avoid buying into overinflated expectations created by the market hype that ignores the limitations of current services. To avoid the inevitable disappointment that follows unfulfilled expectations, network leaders should outline their service requirements, and use these to define evaluation criteria for a balanced analysis of service benefits and limitations.’

Source: Gartner (December 2017)
Enterprise network leaders face enormous challenges adapting and changing their managed WAN services to meet constantly changing business needs for new applications, new offices, more users, cloud services and digital business. Based on hundreds of client inquiries and recent Research Circle surveys, a key obstacle is that traditional network services are too slow in meeting these needs, and network leaders need alternative solutions that can meet their evolving needs faster. Compared to traditional WAN services, managed SD-WAN services (including various WAN connectivity services) are emerging with promises of greater agility, flexibility, control and cost-efficiency.
Gartner recommends that network leaders seeking managed WAN services use end-to-end managed SD-WAN and connectivity services to create agile and cost-effective managed WAN services. However, they must avoid buying into overinflated expectations created by the market hype that ignores the limitations of current services. To avoid the inevitable disappointment that follows unfulfilled expectations, network leaders should outline their service requirements, and use these to define evaluation criteria for a balanced analysis of service benefits and limitations.’

Source: Gartner (December 2017)
Current WAN services take too long to roll out and are too difficult to relocate or terminate, and network leaders are looking for ways to improve this. Network leaders see SD-WAN as a new opportunity to create more agile branch office connectivity due to appliances’ support of “zero-touch-configuration.” Vendors are fueling these expectations with reports of very fast site rollout with reports of 20 to 30 sites deployed overnight, compared to six to 10 sites per week for a traditional managed router service. However, SD-WAN does not change fundamental limitations of connectivity services, for example:
- Fast site deployments are only available for 4G/LTE access services or in cases where the provider already has a wired access service to the building (although in many cases these still require one to two weeks to provision).
- Network leaders who need new wired access services still need to plan for 14 to 90 days (or longer) from order to provisioning.
- All wired branch office connections, private or public, still require network leaders to sign a contract of fixed duration, making it a problem for network leaders to move or terminate a site without financial penalties.
Network leaders who need new WAN sites deployed with short notice should request managed SD-WAN with embedded LTE services. While many providers do not yet offer this service, there are providers in select countries that courier SD-WAN appliances with LTE embedded to customer sites instead of sending a technician. The best-case scenario is only six hours from order placement to on-site delivery of the appliance. Combined with self-service, where the enterprise plugs in the SD-WAN appliance to the LAN and powers up the device, the site can be operational within a day in the best case. However, network leaders who do not want their office staff to plug in the appliance need to plan for up to a week for a technician to be on-site, depending on location.
However, besides expense, the performance limitations of 4G/LTE include lower bandwidth than fiber, lack of geographic coverage and lack of QoS. Also, most of these services are based on using the internet as backhaul to the provider’s internet gateway. This means that, for larger sites and critical applications, network leaders should only employ 4G/LTE connectivity as an interim primary connection until a fiber connection has been deployed.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Because of the performance issues that still plague the internet in most parts of the world, the majority of enterprises are not replacing MPLS with internet services. Instead, based on client inquiries, Gartner estimates that around 60% of global WANs use both internet and MPLS in concert in a hybrid WAN that sends critical application traffic over the MPLS and everything else over the internet.
Enterprise experience has shown that for a global managed hybrid WAN, network planners can obtain at least 30% expense savings compared to traditional managed WAN (see “Cloud Adoption Is Driving Hybrid WAN Architectures” ). Network planners that want to replace their global MPLS with internet should progress selectively, and choose a few sites in areas where the internet is most likely to be of good quality. For these sites, demand a two- to four-month pilot as a condition of signing a new WAN contract. Remember that all internet providers and services are not the same. Use only a select few and do not disaggregate internet providers, as WAN and application performance will suffer.